What is Cryptocurrency mining? How does it work?
3 min read - July 12 by Lizz
Crypto
Cryptocurrency transactions happen in a digital world, but how do we ensure they're secure and trustworthy? Enter cryptocurrency mining, a fascinating process that underpins the security and integrity of many blockchain networks.
1. What is Cryptocurrency mining?
Crypto mining is how new units of cryptocurrency usually called coins are created. As you can imagine, this type of mining doesn't involve callused hands gripping pickaxe handles. Instead, computer processors do all the hard work, chipping away at complex math problems.
Read more: Start Earning Crypto Rewards: Your Guide to Staking
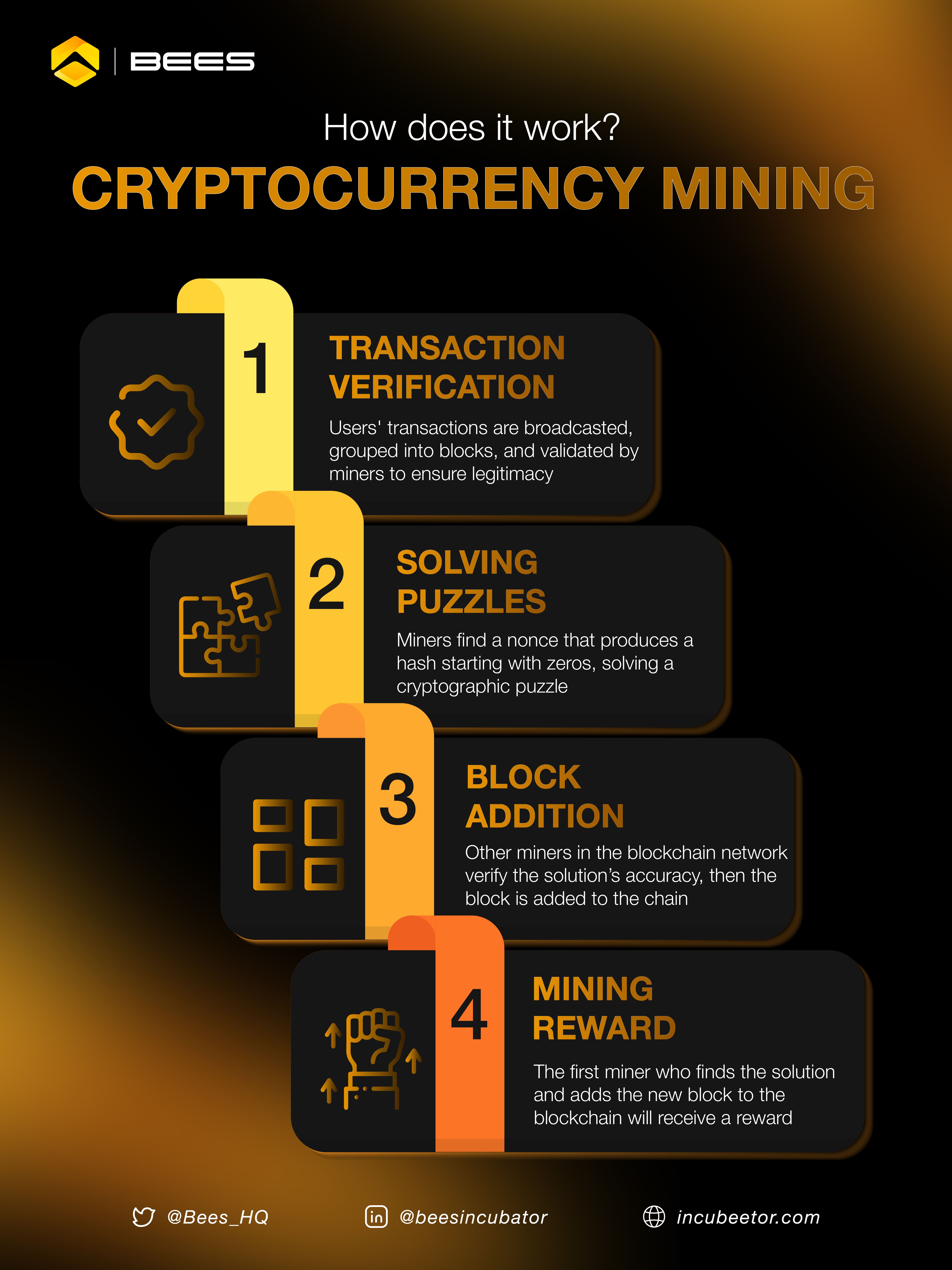
2. How does cryptocurrency mining work?
2.1. Transaction Verification
Imagine a world where anyone can tamper with your bank statements. Thankfully, in the world of cryptocurrency, dedicated individuals called miners act as guardians. When users make transactions, they are broadcasted to the entire network. Miners then group these transactions into a "block." Before adding a block to the permanent ledger (blockchain), miners meticulously verify each transaction to ensure legitimacy and compliance with the network's rules.
2.2. Solving Puzzles
Think of miners as codebreakers competing in a high-stakes puzzle contest. Each block contains a complex mathematical problem that needs to be solved before it can be added to the blockchain. This problem involves finding a specific number called a "nonce." The miners use a cryptographic hash function (like SHA-256 for Bitcoin) to process the block data and the nonce. However, there's a twist! The resulting hash must start with a specific number of zeros, making it incredibly difficult to find the correct solution.
Read more: Understanding the Difference Between Stablecoins & Bitcoin, Ether
2.3. Block Addition
The first miner to crack the code, solving the complex puzzle and generating a valid hash, wins the right to add their block to the blockchain. After the verification of other miners in the blockchain network (with an enough number of miners depending on the principles of the blockchain protocol), this newly block is added to the chain and becomes permanent and unalterable, as any attempt to tamper with it would require altering all subsequent blocks – a near-impossible feat!
2.4. Proof of Work (PoW)
After adding the new block, the rewards are distributed to the miner who first finds the correct nonce and adds a new block to the chain. The rewards may consist of the transaction fees and an amount of newly minted tokens.
Note: The entire mining process revolves around a concept called Proof of Work (PoW). It's a consensus mechanism that ensures the security of the blockchain. By requiring miners to perform computational work (solving the puzzles), PoW makes it incredibly difficult and resource-intensive to manipulate or add fraudulent transactions to the blockchain.
Read more: Benefits of Blockchain
In essence, cryptocurrency mining acts as a distributed security system. It incentivizes miners to participate in the network's verification process, ensuring the integrity and immutability of the digital ledger we call the blockchain.